Introduction to microplate labels and barcodes
About this topic
This topic provides an overview of the labels that you can create for the Microplate Labeler and a general description of barcode types.
Microplate labels
The labels that you create for the Microplate Labeler can contain up to six fields of data, including one barcode field and five human-readable text fields. The following figure shows an example of a typical label that contains two fields: one barcode field and one human-readable field.
Figure Example of a microplate barcode label
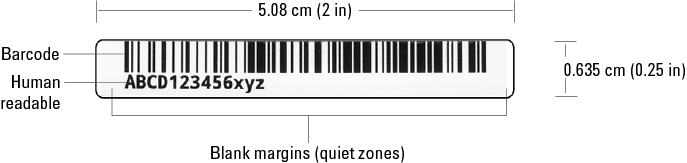 |
In the example, the barcode field has a blank margin (quiet zone) on each end to ensure that a barcode reader can read the barcode successfully. For more details on label design, see About label formats and content.
About barcodes
Barcodes contain information that can be read automatically, facilitating the fast and accurate tracking of microplates in lab automation systems. A barcode reader scans the line patterns, and software converts the encoded patterns into usable information.
The method used for creating a barcode from text is called its symbology. Your choice of symbology depends on the barcode reader used for your application and your laboratory preferences.
The Microplate Labeler can print either linear or two-dimensional (2D) barcodes.
Linear barcodes
A linear barcode is a sequence of parallel bars and spaces of variable widths that are arranged in groups. Each group represents an individual number, letter, or symbol. Within each group, the information is encoded by the relative thicknesses and relative positions of the bars and spaces. A linear barcode symbol contains a leading blank margin (quiet zone), a start character, one or more data characters, a stop character, and a trailing quiet zone.
Figure Example of a linear barcode using Code 128 symbology
 |
Two-dimensional barcodes
2D barcodes are comprised of dots or small bars arranged as a matrix or in a stacked arrangement. The 2D barcodes typically can contain more information than linear barcodes because they encode data in both the vertical and horizontal directions.
Figure Example of a 2D barcode using Data Matrix symbology
 |
Related topics
For information about... | See... |
|---|---|
Label formats and content | |
Barcodes symbologies |