About liquid classes
Liquid Library Editor defined
The Liquid Library Editor provides tools for users with technician or administrator privileges to enter values for properties that affect pipetting speed, accuracy, and precision.
Figure Liquid Library Editor window
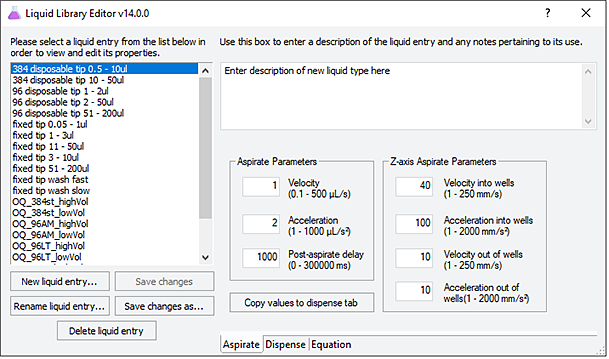 |
Default liquid library entries
The default liquid library entries are provided as examples and thus might only approximate your particular reagents. For the best performance, you should create your own liquid library definitions.
When to use the Liquid Library Editor
You use the Liquid Library to fine-tune the volume aspirated or dispensed by your Bravo Platform.
Liquid classes defined
The values entered into the Liquid Library Editor can be saved as a collection, known as a liquid class. Using liquid classes saves time when writing protocols because you do not have to enter values for the liquid properties every time you create a protocol.
Types of liquid classes
You might want to create different classes for different:
• Types of liquids
For example, water versus DMSO
• Volumes of liquids
For example, 1 µL versus 200 µL
• Liquid operations
For example, washing versus mixing
How liquid classes are stored
Each liquid class is saved as an .xml file in Shared Services storage.
VWorks Plus only. The liquid classes are records of interest. The software automatically logs audit trails for liquid classes that are in the In Validation and Released states. Optionally, the software can log audit trails for these records while they are in the In Development state. For details, see Setting audit trail options.
Using a liquid class
When preparing for a protocol run, you select the liquid class that you want to use. During the run, the liquid class values are referenced for pipetting operations.
Calibrating the Bravo Platform
The Liquid Library Editor also has an equation editor that can be used to calibrate the Bravo Platform.
Related information
For information about... | See... |
|---|---|
Opening the Liquid Library Editor | |
Creating a liquid class | |
Calibrating your pipettor | |
Audit trails and records of interest |